Plumbing vents are essential components of any plumbing system. They ensure the safe and efficient drainage of wastewater, while also preventing sewer gases from entering the building. A plumbing vent diagram provides a visual representation of the layout of the vents, their size and connections to each other and to the plumbing fixtures. In this comprehensive guide, we will discuss what plumbing vent diagrams are, why they are important, how to read them, as well as some tips on installing them correctly.
Plumbing Vent Diagram
Diagram-1
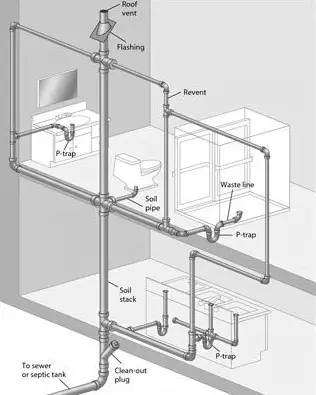
Diagram-2
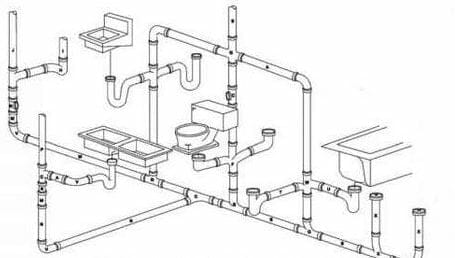
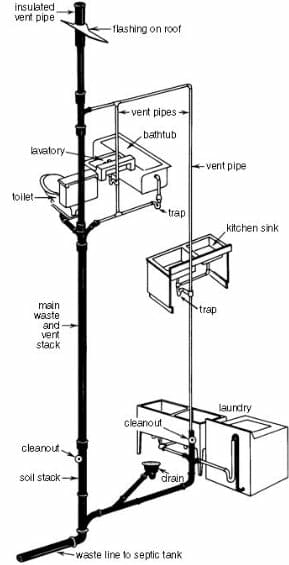
Diagram-3
What is a Plumbing Vent Diagram?
A plumbing vent diagram is a visual representation of how the plumbing pipes in a building connect with each other. It typically shows the route that all pipes take from the main stack or drainpipe to each individual fixture, such as toilets and sinks. The diagram also indicates which type of pipe material should be used for each connection, as well as where and how far apart each pipe should be installed in order to ensure proper drainage.
Why Are Plumbing Vents Important?
Plumbing vents help prevent sewer gases from entering your home by providing an air channel that allows pressure within the pipes to equalize between high-pressure areas (such as sinks) and low-pressure areas (such as toilets). Without these vents, wastewater would not be able to flow freely through your home’s piping system due to pressure imbalances caused by unequal amounts of water being used at different fixtures at different times. Additionally, without proper ventilation for air circulation within your pipes, you risk developing blockages due to built-up sludge or stagnant water in certain sections of your pipework.
How does plumbing vents work
Plumbing vents are an important component of a building’s plumbing system, as they serve several important functions. Here’s a brief overview of how plumbing vents work:
- Preventing sewer gases from entering the building
- Every time a plumbing fixture (such as a sink, toilet, or bathtub) is used, water and waste flow through the drain and into the building’s sewer or septic system.
- Without a vent, the air in the drain pipe is displaced by the water and waste, creating a vacuum that can suck sewer gases (such as methane and hydrogen sulfide) back into the building through the drain.
- A plumbing vent provides a way for the displaced air to escape, allowing fresh air to flow into the drain pipe and preventing sewer gases from entering the building.
- Allowing air to flow through the pipes for proper drainage
- As water and waste flow through the drain pipes, air is needed to help push the water and waste along and prevent blockages.
- Without a vent, the drain pipe can become “airlocked,” meaning that the water and waste cannot flow properly and can create clogs.
- A plumbing vent provides a way for air to enter the drain pipe, allowing water and waste to flow freely and preventing clogs.
In summary, a plumbing vent works by allowing air to enter the drain pipe, which prevents sewer gases from entering the building and helps water and waste flow properly through the plumbing system. A properly designed and installed plumbing vent system is essential for the safety and proper functioning of a building’s plumbing system.
Tips For Installing Plumbing Vents
When installing your own plumbing vents it’s important to keep several key points in mind: Make sure that all connections are secure and properly sealed with plumber’s putty or silicone sealant before testing for leaks; use only approved materials for each type of fitting; check all measurements against local codes before beginning work; avoid using too many elbows or bends in any given run if possible in order to maximize airflow efficiency; install vertical vents so they extend above roof level where possible.
Components of a plumbing vent system
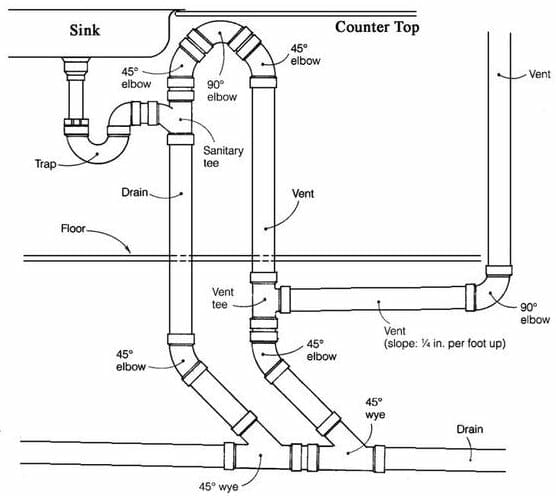
The plumbing vent system consists of various components that work together to allow for proper drainage and prevent the entry of sewer gases. Here are the main components of a plumbing vent system:
Vent pipes
These pipes run vertically from the drain system and extend above the roof line of the building. Vent pipes allow for air to enter the plumbing system to equalize pressure and promote proper drainage. They also allow for sewer gases to escape out of the building, preventing them from entering living spaces. Vent pipes are usually the same size as the drain pipes they serve.
Vent stacks
Vent stacks are large-diameter vent pipes that serve as the main pathway for venting multiple vent pipes. They run vertically through the building and connect to the vent pipes that serve each plumbing fixture.
Roof flashing
This component is installed on the roof around the base of the vent pipe to prevent water from entering the building. The flashing is typically made of metal and provides a seal between the pipe and the roof.
Fittings
Fittings, such as elbows, T-joints, and couplings, are used to connect the vent pipes and create the necessary plumbing configurations. These fittings are made from the same materials as the pipes and are typically secured using pipe cement.
Vent pipes are sized according to the diameter of the drain pipe they serve. In general, vent pipes should be at least 1 1/2 inches in diameter, and larger pipe diameters may be required for larger drain pipes or longer distances between fixtures and vents. Vent pipes are typically installed vertically and should be at least 6 inches above the roof line. The distance between the fixture and the vent pipe must also be considered when sizing and installing the vent pipes.
There are two main types of vent pipes
air admittance valves (AAVs) and traditional vent pipes. AAVs are mechanical devices that allow air to enter the plumbing system when a fixture is used and then close when the fixture is not in use. Traditional vent pipes are always open to the atmosphere and allow air to enter the plumbing system at all times. Both types of vent pipes have their own benefits and drawbacks, and the choice between them will depend on the specific needs of the plumbing system.
Latest Post
- Are Sharkbite Fittings Legal in California
- 3 inch or 4 inch flue for water heater?
- Briggs Liberty Ultracast Bathtub Reviews
- Ao Smith vs Bradford White Gas Water Heaters – Which One Best?
- The Americast Bathtub Reviews – Top Quality Bathtub
- Sewage Smell Coming From Air Vents? – Cause & Solution
- Types Of Bathroom Sink Drain Stoppers
- Plumbing Vent Diagram [3 Visible Diagram]
- How To Purge Air From Gas Line On Water Heater – Step By Step Guideline
- Do SharkBite Fittings Reduce Water Flow?
- Dual Shower Head Plumbing Diagram
- Boiler Drain vs Hose Bibb: Choosing Right Option for Your Plumbing Needs
- SDR 35 vs Schedule 40 – Which PVC Pipe Comes Out on Top?
- Air Scrubber By Aerus Reviews
- HVAC Tape VS Duct Tape: The Ultimate Showdown!
- Accidentally Flushed Washcloth Down Toilet Septic System? Complete Solution
- J Bolt Vs Anchor Bolt: Get The Main Difference In 2023
- Long Sweep 90 Vs Short Sweep: Which Is Better For You?
- InSinkErator Hot Water Dispenser Leaking? – Complete Solution
- American Standard Cambridge Vs Princeton Bathtub: What’s The Difference In 2023?





















