To layout plumbing for a bathroom, first plan the location of fixtures, then install the main drain and vent lines. Ensure proper pipe connections to maintain efficient water flow.
Planning your bathroom plumbing layout is essential for a functional and efficient space. Start by determining where you want to place fixtures like the sink, toilet, and shower. Proper planning helps to minimize the distance between the water supply and drainage points, reducing potential issues.
Once the fixture locations are decided, install the main drain and vent lines to ensure proper waste removal and ventilation. Properly connecting all pipes will prevent leaks and maintain water flow efficiency. Good plumbing layout minimizes future maintenance and ensures a smooth bathroom operation. A well-thought-out plan saves both time and money in the long run.
Planning The Layout
Planning the layout for bathroom plumbing is crucial. Proper planning ensures everything works smoothly. It also prevents future issues. This guide will help you understand how to layout plumbing for your bathroom.
Assess Space
Start by assessing the available space. Measure the dimensions of your bathroom. Make a rough sketch of the area. Include the locations of doors and windows. This helps in planning the placement of fixtures. Ensure you have enough room for each element.
Think about where you want the sink, toilet, and shower. Proper placement can make a big difference. A well-planned layout can save you from costly mistakes. Use a measuring tape and mark the spots. Consider the distance between the fixtures. Leave enough space for comfortable use.
- Measure the bathroom dimensions.
- Sketch the layout.
- Mark doors and windows.
- Plan fixture placement.
- Ensure comfortable spacing.
Check if you need to move any walls. This can give you more options. Moving walls can be expensive, so plan wisely. Consider the height of the ceiling too. This can affect the placement of certain fixtures.
Consider Plumbing Codes
Plumbing codes are essential for safety. These codes ensure that plumbing systems work correctly. Check the local plumbing codes before starting your project. These codes vary by location. Understanding them is crucial for compliance.
Most codes specify the distance between fixtures. They also set rules for the type of pipes to use. Using the right materials is important. It ensures the longevity of your plumbing system. Follow the codes to avoid fines and penalties.
| Fixture | Minimum Distance |
|---|---|
| Toilet to Sink | 15 inches |
| Shower to Sink | 20 inches |
| Toilet to Wall | 18 inches |
Consult a professional if you are unsure. They can help you understand the codes better. Proper compliance ensures a safe and efficient plumbing system. Keep the codes handy during your project. This will help you stay on track.
Choosing Fixtures
Planning your bathroom layout is crucial. Choosing the right fixtures ensures functionality and style. It’s important to select fixtures that suit your needs and space. This guide will help you understand your options.
Toilet Options
Toilets come in various styles and types. The two-piece toilet is the most common. It has a separate tank and bowl. They are easy to repair and budget-friendly. One-piece toilets have a sleek design. They are easier to clean but can be more expensive.
Wall-mounted toilets save space. They offer a modern look. However, they require strong wall support. Composting toilets are eco-friendly. They use little to no water. This makes them ideal for off-grid living.
| Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Two-Piece | Affordable, Easy to repair |
| One-Piece | Sleek design, Easy to clean |
| Wall-Mounted | Space-saving, Modern look |
| Composting | Eco-friendly, Low water use |
Sink Styles
Sinks are a key part of your bathroom. Pedestal sinks are elegant and save space. They are perfect for small bathrooms. Vessel sinks sit on top of the counter. They offer a unique and stylish look. These are ideal for modern designs.
Undermount sinks are installed under the counter. This makes cleaning easy. They provide a seamless look. Wall-mounted sinks free up floor space. They are good for small bathrooms. Console sinks have a vintage feel. They also offer extra counter space.
- Pedestal sinks: Elegant, Space-saving
- Vessel sinks: Unique, Stylish
- Undermount sinks: Easy to clean, Seamless look
- Wall-mounted sinks: Floor space saver
- Console sinks: Vintage feel, Extra counter space
Shower Vs. Bathtub
Choosing between a shower and a bathtub depends on your needs. Showers are quick and efficient. They save water and space. Walk-in showers are accessible and stylish. They are ideal for small bathrooms.
Bathtubs offer relaxation. They are great for soaking and unwinding. Freestanding tubs are a statement piece. They add luxury to any bathroom. Built-in tubs are practical. They fit well in most spaces. Jacuzzi tubs provide a spa experience at home.
| Option | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Shower | Quick, Efficient, Saves water |
| Walk-in Shower | Accessible, Stylish |
| Bathtub | Relaxing, Good for soaking |
| Freestanding Tub | Luxury, Statement piece |
| Built-in Tub | Practical, Fits in most spaces |
| Jacuzzi Tub | Spa experience at home |
Water Supply Lines
Designing the plumbing layout for your bathroom is essential. Proper water supply lines ensure efficient and reliable water flow. This guide will help you understand the basics of water supply lines, covering both cold and hot water lines.
Cold Water Lines
Cold water lines are crucial for your bathroom. They supply fresh water to all fixtures. The main water line brings cold water from the main supply. Each fixture has a branch line that connects to the main line.
Here are some key points about cold water lines:
- Main line: This is the primary source of cold water.
- Branch lines: These connect the main line to various fixtures.
- Shut-off valves: Installed near each fixture for easy maintenance.
Below is a simple table showing the cold water distribution:
| Fixture | Pipe Size | Connection Type |
|---|---|---|
| Shower | 1/2 inch | Threaded |
| Sink | 1/2 inch | Threaded |
| Toilet | 1/2 inch | Threaded |
Always use pipes that match the fixture’s requirements. Proper pipe size ensures adequate water pressure. Threaded connections are common and reliable.
Hot Water Lines
Hot water lines deliver heated water from your water heater to the fixtures. These lines are essential for comfort and hygiene. Like cold water lines, hot water lines have a main line and branch lines.
Key points about hot water lines:
- Main line: Connects the water heater to the bathroom.
- Branch lines: Distribute hot water to each fixture.
- Insulation: Important to maintain water temperature.
Below is a simple table showing the hot water distribution:
| Fixture | Pipe Size | Connection Type |
|---|---|---|
| Shower | 1/2 inch | Threaded |
| Sink | 1/2 inch | Threaded |
| Bathtub | 1/2 inch | Threaded |
Ensure that hot water pipes are well-insulated. This keeps the water hot and saves energy. Use the correct pipe size and connection type for each fixture. This guarantees a steady supply of hot water.
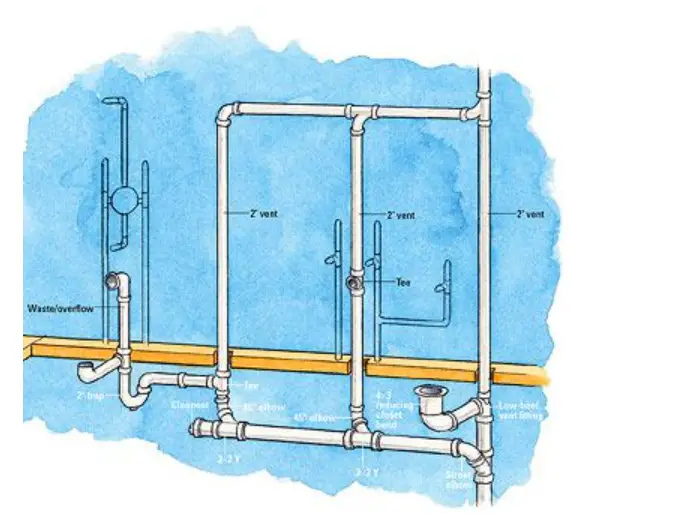
Drainage System
Planning the plumbing for a bathroom is a crucial step in home improvement. A well-designed drainage system ensures smooth water flow and prevents potential problems. This guide will help you understand the basics of setting up the drainage system, focusing on sewage lines and vent pipes.
Sewage Lines
Sewage lines carry waste water from the bathroom to the main sewer. It’s important to plan these lines carefully to avoid any blockages or leaks. Here are some key points to consider:
- Use PVC pipes for the sewage lines. They are durable and easy to install.
- Ensure the pipes have a slight slope. This helps water flow naturally towards the main sewer.
- Install clean-out points. These allow easy access for maintenance and blockages removal.
Position the toilet closest to the main sewage line. This reduces the risk of clogs and ensures efficient waste removal. Use a T-joint to connect the toilet to the main sewage line. This joint should be at a 45-degree angle to facilitate smooth flow.
For sinks and bathtubs, use smaller diameter pipes. Connect these to the main sewage line using Y-joints. These joints help in maintaining the flow direction and prevent any backflow.
Vent Pipes
Vent pipes are essential for maintaining proper airflow within the drainage system. They prevent water from being siphoned out of traps, which can lead to unpleasant odors. Here are some important aspects of vent pipes:
- Install vent pipes vertically. This allows gases to escape and air to enter the system.
- Connect the vent pipes to the main sewage line. This should be done above the highest fixture.
- Ensure the vent pipes extend above the roofline. This prevents any gases from re-entering the house.
Use T-joints to connect vent pipes to the main sewage line. These joints should be placed at least six inches above the highest fixture. This ensures that water does not block the airflow.
For multiple fixtures, you can use a common vent. Connect this common vent to the main vent stack. This setup simplifies the plumbing layout and reduces the number of pipes needed.
Pipe Materials
Properly laying out plumbing for a bathroom is crucial for functionality and safety. Choosing the right pipe materials plays a significant role in this process. Different materials offer varied benefits and are suitable for different applications. Here, we will discuss three common pipe materials: PVC, Copper, and PEX.
Pvc
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) pipes are a popular choice for bathroom plumbing. They are lightweight and easy to install. PVC pipes are also resistant to corrosion and chemicals. They are often used for drain, waste, and vent pipes. One of the key benefits is their affordability.
Advantages of PVC pipes include:
- Easy to handle and cut
- Resistant to corrosion
- Cost-effective
- Long-lasting
Disadvantages of PVC pipes include:
- Not suitable for hot water lines
- Can become brittle over time
- Not as strong as metal pipes
Applications of PVC pipes:
| Application | Usage |
|---|---|
| Drainage | Excellent for waste removal |
| Ventilation | Used in vent pipes |
| Cold water supply | Suitable for cold water lines |
Copper
Copper pipes have been used in plumbing for many years. They are known for their durability and reliability. Copper is also resistant to bacteria, making it a safe option for water supply lines. These pipes can handle both hot and cold water.
Advantages of copper pipes include:
- Very durable and long-lasting
- Resistant to bacteria
- Handles high water pressure
- Can be used for hot and cold water
Disadvantages of copper pipes include:
- Expensive compared to other materials
- Requires skilled labor for installation
- Can corrode if water is too acidic
Applications of copper pipes:
| Application | Usage |
|---|---|
| Water supply | Ideal for hot and cold water lines |
| Heating systems | Used in heating systems |
| Refrigeration | Common in refrigeration applications |
Pex
PEX (Cross-linked Polyethylene) pipes are a modern alternative to traditional materials. They are flexible and can be easily bent around corners. PEX pipes are resistant to scale and chlorine, making them ideal for water supply lines. They are also more affordable than copper.
Advantages of PEX pipes include:
- Flexible and easy to install
- Resistant to scale and chlorine
- Cost-effective
- Can handle both hot and cold water
Disadvantages of PEX pipes include:
- Can be damaged by UV light
- Not recyclable
- May leak if not installed properly
Applications of PEX pipes:
| Application | Usage |
|---|---|
| Water supply | Great for hot and cold water lines |
| Radiant floor heating | Used in underfloor heating systems |
| Snow melting | Used in outdoor snow melting systems |
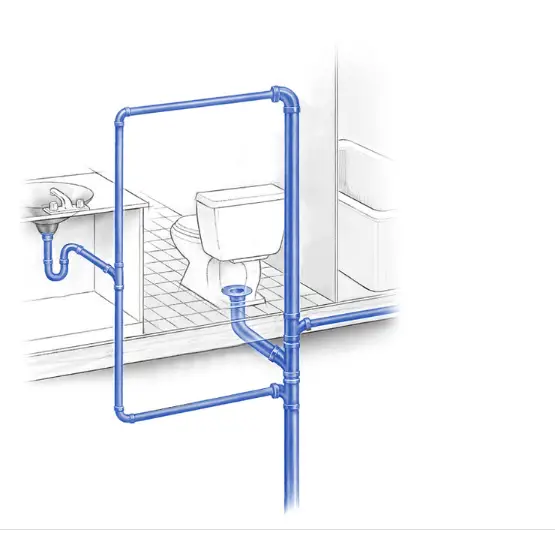
Creating A Plumbing Diagram
Creating a plumbing diagram for your bathroom is a crucial step in ensuring a smooth renovation or construction process. It helps you visualize the placement of pipes, fixtures, and other essential components. By understanding how to layout plumbing correctly, you can avoid costly mistakes and ensure efficient water flow. This guide will walk you through the steps of sketching the layout and labeling the components properly.
Sketching Layout
Start by drawing a rough sketch of your bathroom. This layout sketch should include all walls, doors, and windows. Measure the dimensions of your bathroom to ensure accuracy. Place the main fixtures like the toilet, sink, and shower on the sketch.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Toilet placement: Ensure it is near the main drain line.
- Sink placement: Position it close to the water supply lines.
- Shower placement: Make sure it has proper drainage access.
Next, draw the pipe routes connecting these fixtures. Use different colors or lines to distinguish between hot and cold water lines. Include vent pipes to prevent sewer gases from entering your home. The diagram should clearly show how these pipes will run through the walls and floors.
Labeling Components
Once the layout is sketched, start labeling each component. Clearly mark each pipe and fixture in your diagram. Use labels such as “Hot Water Line,” “Cold Water Line,” “Drain Pipe,” and “Vent Pipe.“
Here is a simple table to help you organize the labels:
| Component | Label |
|---|---|
| Hot Water Line | HW |
| Cold Water Line | CW |
| Drain Pipe | DP |
| Vent Pipe | VP |
Use these abbreviations on your sketch. This will help you and any contractors understand the plan easily. Double-check your labels to ensure no mistakes. Proper labeling ensures that everyone involved knows exactly what each component represents.
Installation Process
Plumbing is a crucial part of any bathroom. Proper layout ensures everything works smoothly. This guide will help you understand the installation process. Follow these steps to achieve a perfect plumbing setup.
Cutting Pipes
Cutting pipes is a vital step in plumbing. You need to measure the pipes carefully. Make sure you have the right tools.
Here are the tools you need:
- Pipe cutter
- Measuring tape
- Marker
- Hacksaw (optional)
First, measure the length of pipe you need. Use the measuring tape for this. Mark the cutting spot with a marker. Make sure the mark is clear and visible.
Next, use the pipe cutter. Place the cutter on the mark. Rotate the cutter around the pipe. Keep rotating until the pipe is cut. This ensures a clean and even cut.
If you use a hacksaw, make sure to cut straight. Hold the pipe firmly. Smooth the edges with sandpaper. This will remove any burrs. Smooth edges help in better fitting and joining.
Joining Techniques
Joining pipes is another important step. There are various techniques for joining. Each has its own benefits.
Here are common joining techniques:
- Solvent welding
- Compression fittings
- Soldering
- Push-fit fittings
Solvent welding uses a special glue. Apply the glue to both pipe ends. Push them together. Hold for a few seconds. The glue creates a strong bond.
Compression fittings are easy to use. Slide the fitting onto the pipe. Tighten with a wrench. This creates a secure join. No need for glue or heat.
Soldering requires a torch. Heat the pipe ends. Apply solder wire. The heat melts the solder. This seals the pipes together. Soldering is strong and durable.
Push-fit fittings are the easiest. Push the pipe into the fitting. It clicks into place. No tools needed. Great for quick repairs.
Testing The System
Installing plumbing in a bathroom can be tricky. It’s important to check for leaks and ensure proper water flow. Testing the system helps avoid future problems. Let’s explore how to test your plumbing system effectively.
Leak Checks
Leaks can cause damage. It’s important to check for them. Here are some steps to follow:
- Turn off all water sources.
- Inspect all pipes and joints for any signs of moisture.
- Feel around pipes for wet spots.
For a more detailed check, a pressure test can be done. This helps identify hidden leaks. Follow these steps:
- Close all water outlets.
- Attach a pressure gauge to the system.
- Increase the pressure to the recommended level.
- Monitor the gauge for 15 minutes.
If the pressure drops, there might be a leak. Investigate and repair any leaks found. Regular leak checks can prevent costly repairs.
Water Flow Tests
Proper water flow is crucial. It ensures all fixtures work well. Here’s how to test water flow:
- Turn on all faucets one by one.
- Check the pressure and flow rate.
- Ensure water flows smoothly without splashing.
If any faucet has low pressure, inspect for blockages. Here’s a simple table to help track flow rates:
| Fixture | Expected Flow Rate | Actual Flow Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Sink | 1.5 GPM | ___ |
| Shower | 2.5 GPM | ___ |
| Toilet | 1.6 GPF | ___ |
Fill in the actual flow rates. Compare them to the expected rates. Adjust or repair any fixtures with low flow. Consistent water flow ensures a functional bathroom.

Credit: www.pinterest.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Start Plumbing Layout?
Begin by planning the pipe routes and fixture locations. Use a floor plan to mark these. Ensure water supply and drainage lines are accessible and follow local codes.
What Tools Are Needed For Bathroom Plumbing?
You’ll need pipe cutters, a wrench, pipe fittings, Teflon tape, and a pipe wrench. Also, include a level and measuring tape for accuracy.
How To Ensure Proper Drainage In A Bathroom?
Ensure pipes slope downward at a 1/4 inch per foot. This prevents clogs and ensures efficient drainage. Check local codes for specific requirements.
Can I Do Bathroom Plumbing Myself?
Yes, with the right tools and knowledge, you can. However, complex tasks might require a professional. Always check local codes and regulations.
Conclusion
Properly laying out plumbing for a bathroom is crucial for functionality and efficiency. Follow these steps to ensure a smooth installation process. Remember to plan thoroughly, use quality materials, and consult professionals if needed. A well-executed plumbing layout will save you time, money, and future headaches.
